Skin diseases in cats

Skin Diseases
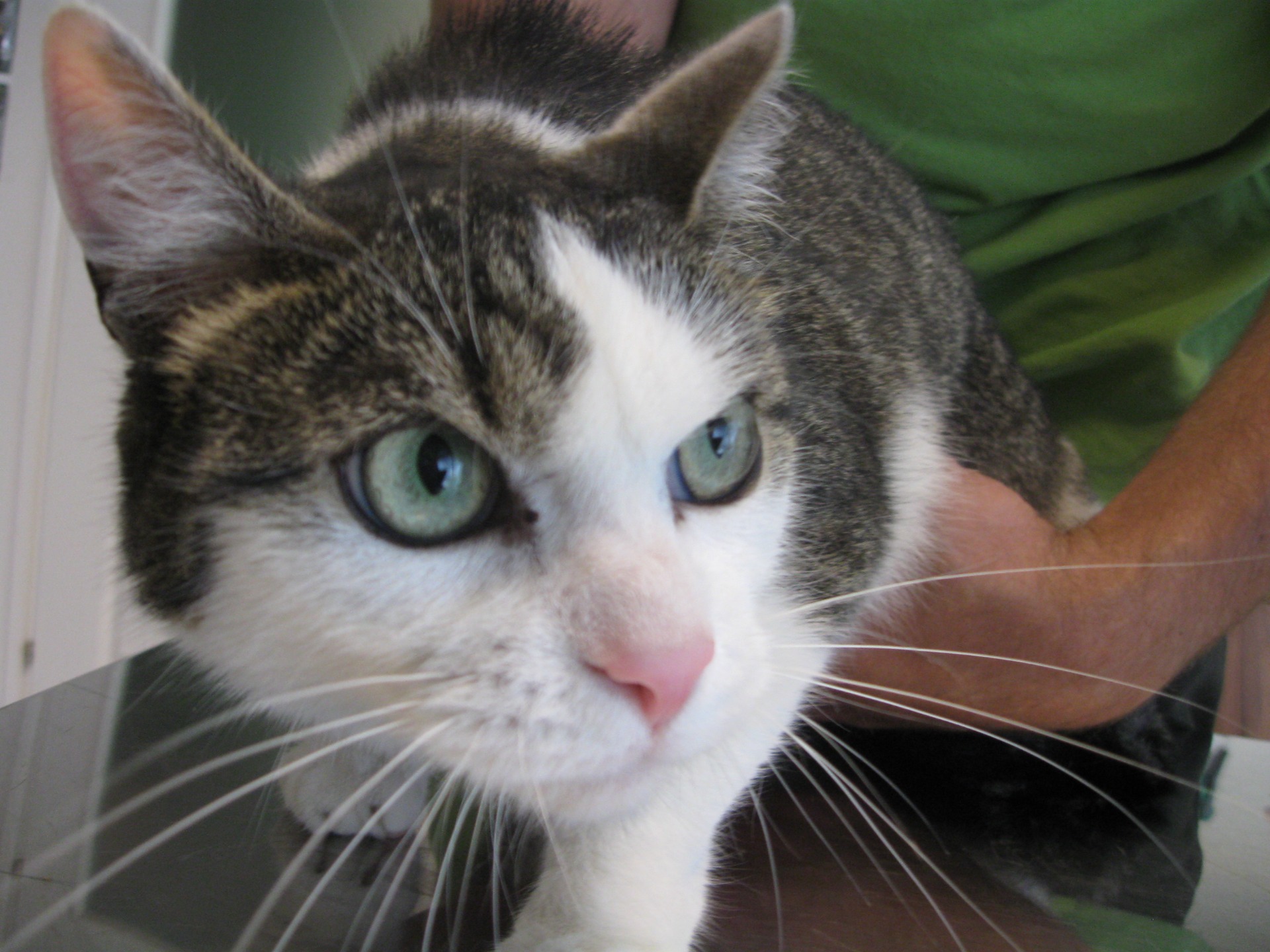
Skin Inflammation (Dermatitis)
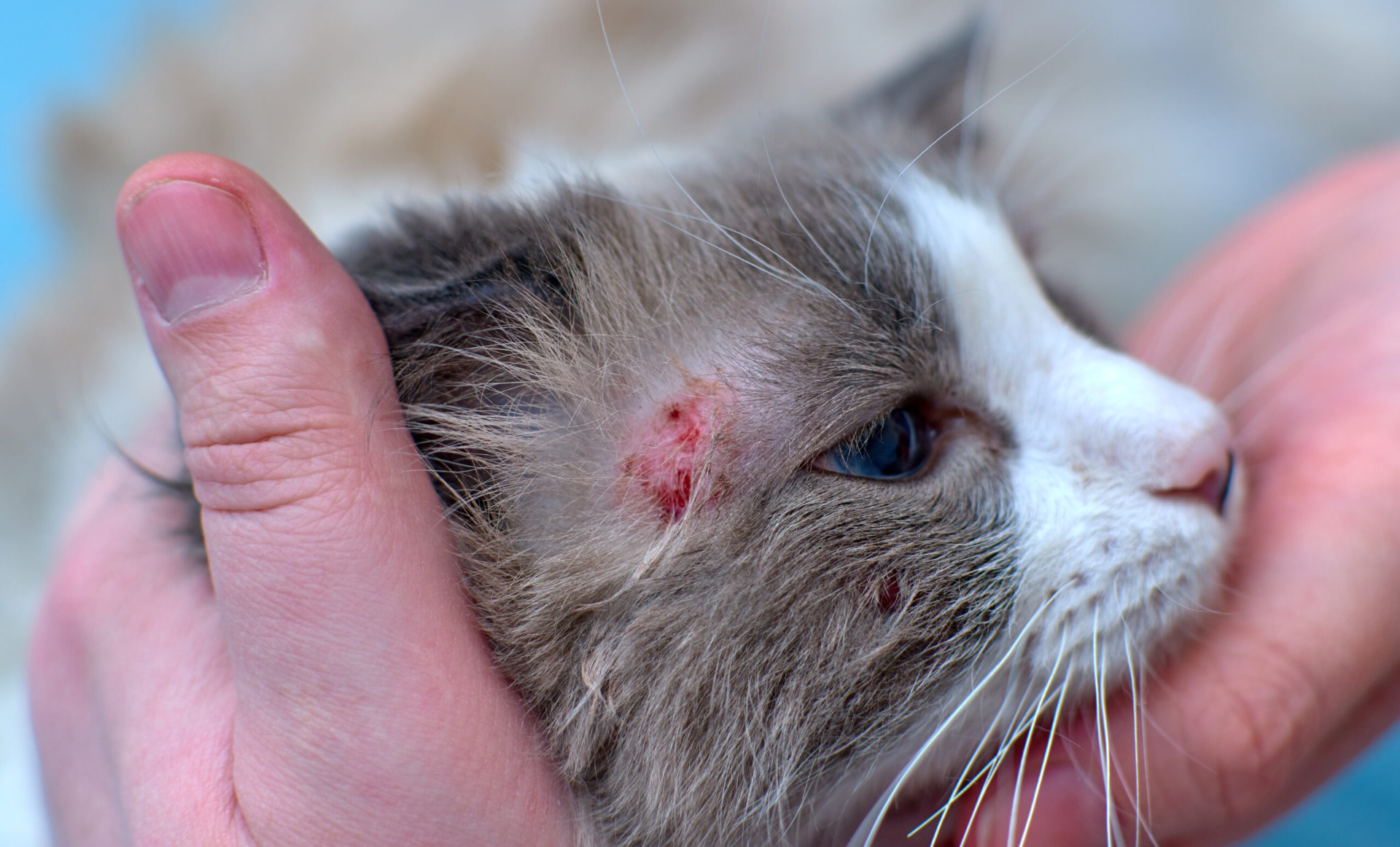
Introduction:
The outer skin is the largest organ of animals, and dermatological problems are very challenging for animals, since often a simple skin problem can be the cause of even more serious illnesses.
Symptoms:
Pruritus, tenderness, and secondary scarring caused by constant scratching are most commonly encountered with allergic dermatitis. In the case of bacterial skin inflammation (pyoderma), inflammation of the skin is accompanied by bleeding and purulent discharge.
Diagnosis:
Skin symptoms are relatively poor, but they can develop for a number of reasons, so skin scraping is often of great importance in establishing accurate diagnosis. During the laboratory test, parasitological examination, bacterial culture and sensitivity testing, and fungal cultures may be requested. In the case of allergic dermatitis, blood tests or skin allergy testing may be required. For secondary skin lesions, it is very important to settle the basic problem before treatment.
Treatment:
For allergic dermatitis, treatment is based on the affecting allergen. For bacterial dermatitis, therapeutic bathing, skin nutrition supplements, and possibly targeted antibiotics may be required for treatment.
Ringworm (Dermatomycosis)

Introduction:
We often see dermatomycosis in pets as there are many environmental factors that can cause it. Things like local skin trauma (e.g. wounds caused by scratching or chronic moisture), a weak immune system (e.g. a prolonged illness), or a long-lasting course of antibiotics can increase the possibility of infection.
Symptoms:
In cases of dermatomycosis, the skin is often dry and flaky, but not itchy. Local and, in some cases, widespread alopecia can be seen. A red ring appears around the infected lesions which spread outward in a circular pattern.
Diagnosis:
Skin scraping for microscopic examination is most often used to detect and identify the possible fungus. The sample is also frequently sent for culture which helps to distinguish which antifungal medications will be effective against the infection.
Treatment:
The most common form of dermatomycosis is microsporidiosis, caused by Microsporum canis. However, there is a vaccine which has been proven to successfully eliminate it. In addition to antifungal drug therapy, there are many other treatments (e.g. topical treatments, environmental decontamination, etc.)
that should be given to ensure proper healing.
