Oral problemes
ORAL PROBLEMS
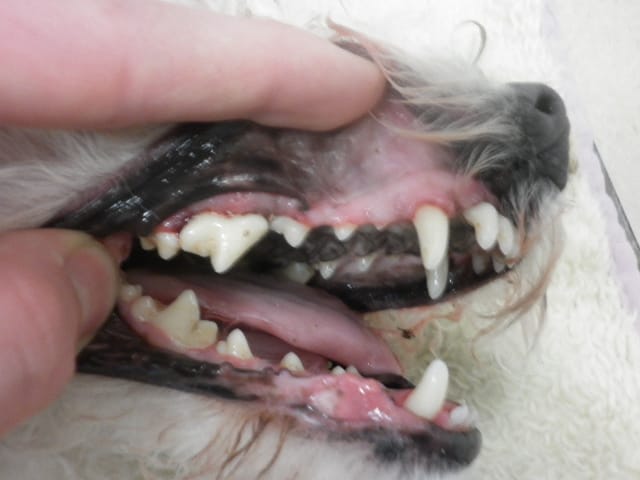
PLAQUE – Cremor dentalis
Introduction:
Plaque is a very common problem of the carnivore animals. The alkaline mouth ph and the bacteria flora of the mouth is definitely favourable for fur forming on the surface of the teeth, then the plaque.
Symptoms:
Not just oral hygienic problems, but gum inflammation is caused by the plaque, and the causative agents which get into the blood circulation along the inflamed gum, may even get to the further organs.
The first symptom of the gum inflammation is redness of the gums rim which bleeds easily. In case of acute gum inflammation, irreversible ulathopy may develop. The teeth may loosen due to the plaque.
The bacteria getting to the blood circulation from the alveolic inflammation often cause inflammation on the heart valves, which may lead to heart valve insuffiency. Inflamed plexus in the kidneys, liver or in other organs may occur.
Prevention, treatment:
Prevention is very important! The smaller dog breeds are more susceptible to have plaque, so the prevention should be started in the puppy age. At first, it is sufficient to have the puppy let us touch its mouth or teeth. There are more ways to defend against plaque forming, but the most important one is the mechanical tooth-cleaning, toth-brushing. There are plaque-forming reducer nutrition supplements. Some kinds of dry foods are good against plaque. Chewing tapes can also be used.
If our pet is succeptible for having plaque, it can only be detained, and not totally prevented. Some animals let the mild type of plaque be picked from their teeth while they are awake, but proper plaque removal is only possible with ultrasound depuration, which is only tolerated by animals while they are drugged. Besides ultrasound plaque removal, local treatment of gum inflammation and antibiotics are often necessary. In some cases, the treatment of diseases in further organs is needed.
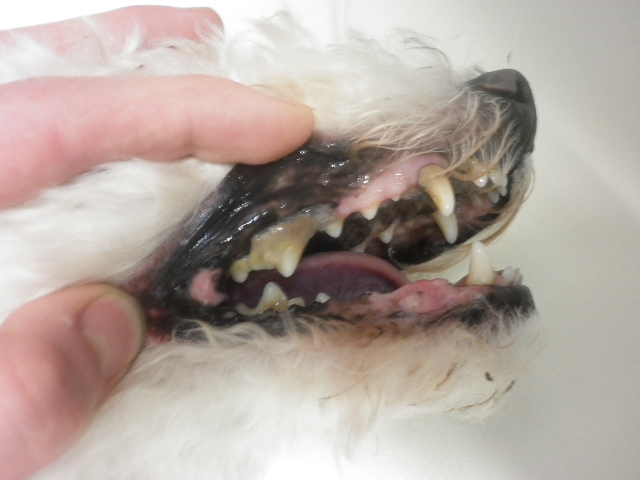
Gum overgrowth (Epulis)
Introduction:
Overgrowth of the gum is a benign process. It is a common problem in short nosed breeds.
Symptoms:
At first, it is an aesthetic problem, then the food leftovers stay in the areas under the overgrowth which causes bad breath and gum inflammation, plaque may evolve from the permanent fur. Not rarely, the epulis leans on the tooth, causing chewing problems, one-sided chewing and when the animal bites on the epulis, it causes bleeding. In extreme cases, the epulis may grow totally on the tooth.
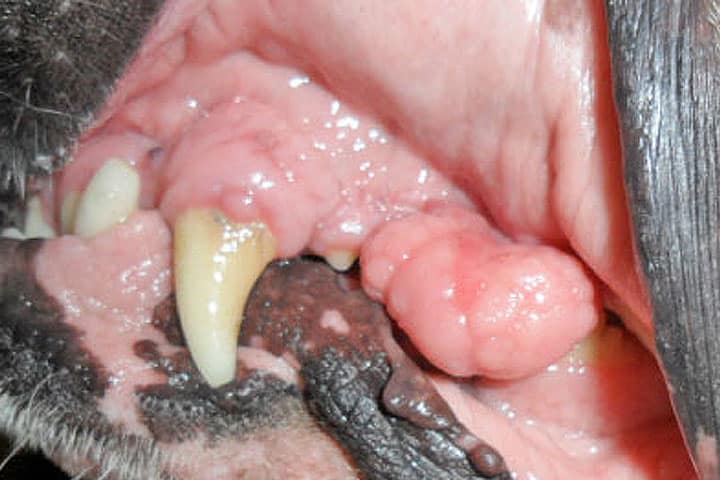
Permanent milk-teeth (PERSISTENTIA DENTIS)
Introduction:
In small dogs, the problem of having the permanent tooth grown next to the milk tooth is not rare. Normally, the change of teeth starts when the puppies are 3-4 months old, and ends until they are 6 months old. First, the upper then the lower incisors change. The problem is most common with the long rooted cuspids. In breeds with narrow jaw-bones (e.g. Yorkshire terrier), problems with the change of incisors and grinders may occur.
Symptoms:
If the milk cuspids do not fall out, it may hold down the proper scissory shut of the permanent tooth, and the food leftovers may stay inside in those areas, so it may lead to gum inflammation and later plaque.
Treatment:
If the double dentation does not start until the 8th months of age, pulling out the milk teeth is recommended, which should be made with the dog drugged.
PAPILLOMATOSIS
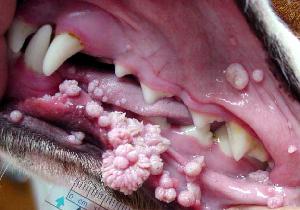
Introduction:
In young dogs, especially if their ability of defense does not work properly, it is not rare that white cauliflower-like accessions grow on the oral mucosa. It is caused by Papova-virus. The organization produces anti-bodies agains Papova-virus, so the accessions may disappear without treatment.
Symptoms:
The viral accessions only cause aesthetic probems, but if they are close to the chewing surface, they may cause one-sided chewing or bleeding if the dog bites on them. Besides the mucosa of the mouth, viral accessions may develop next to the anus or around the genitals.
Treatment:
In milder cases, no treatment is needed. If many papillomas have evolved, immune strengtheners are recommended to use. In case of bigger accessions, they should be burned by thermocauter. If the papillomatosis is very severe, after removing the accessions, autovaccine may be prepared from their scrubbing.
