Gut problemes
GUT PROBLEMS
Gut inflammation (ENTERITIS)

Introduction:
Gut inflammation can evolve due to many reasons. It may be caused by infectiong agent (bacteria, virus, parasite, fungus), spoiled food, toxic material (e.g. chemicals, drugs which irritate the gut mucosa) or food intolerance.
Symptoms:
Symptoms are the following: liquid faeces, possibly loss of housetrainedness, vomiting. In case of colon inflammation, mostly pappy, soft faeces can be notices.
Diagnosis:
Usually, a diagnosis can be made according to the anamnesis, symptoms, physical examination; but sometimes stool-examination or abdominal ultrasound test is needed to get the exact diagnosis.
Treatment:
In all cases, fasting, tea, diet and causal treatment (pl. antibiotics), possibly probiotics. In severe cases, if the patient has lost a big amount of liquids with diarrhea or vomiting, an infusion may be needed.
Gut-flora shifting (DYSBIOSIS)
Introduction
The gut flora of animals adjusts to their nutrition, and normally, if the composition of their food does not change, the bacteria in the guts mould balance and help the proper digestion. In case of sudden food change, or under the effects of medicines affecting gut bacteria (e.g. antibiotics), the balance of the gut flora may turn over, dysbiosis happens.
Symptoms:
Mild or diarrheic stool, absorption disorders, lack of vitamins, weight loss.
Diagnosis:
It can be stated with stool tests whether the symptoms are caused by bacteria or the difference of the normal gut flora.
Treatment:
Probiotics, diet, perhaps vitamin supplement.
Intestinal volvulus
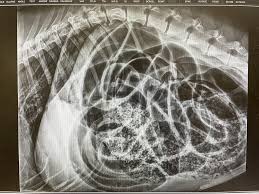
Bevezetés:
Fortunately, it is a rare problem, with a doubtful prognostication.
Symptoms:
Suddenly evolving abdominal pain, vomiting, quickly worsening condition, acute collapse of the blood circulation, dry and purplish mucosa, usual weakness.
Diagnosis:
Profound physical examination and abdominal ultrasound is indispensable.
Treatment:
The only way to treat it is the surgery, within a few hours. Usually gut excising and careful post-treatment is needed.
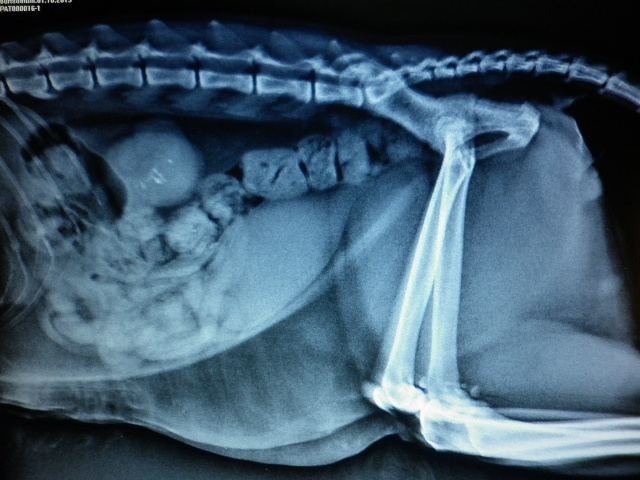
GUT DISCLOSURE (ILEUS)
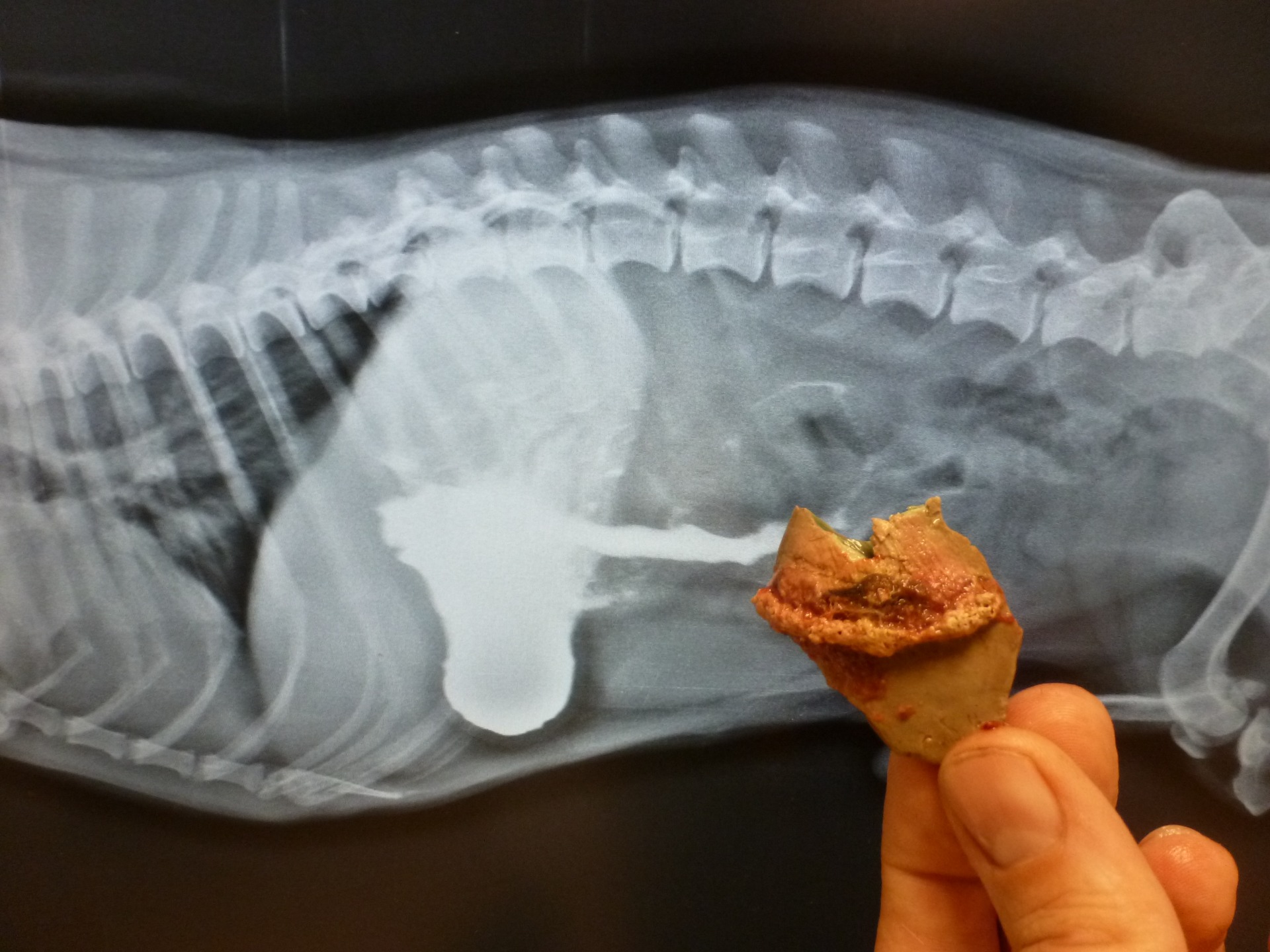
Introduction:
The most common reason of ileus is swallowing objects, which can block the gut cavity. Less common is the gut obliterated by disease processes starting from the gut wall, mostly gut tumour may block the gut cavity. Rarely, other problems of the stomach cavity may compress the gut cavity from outside, causing ileus.
Symptoms:
The typical symptom of total ileus is vomiting. The closer the obliteration to the stomach is, the heavier the vomiting is. After a few time, there is no stool. Lack of appetite, abdominal pain, abdominal cramps, gassy guts, ever bigger stomach, deteriorative condition, dejectedness is common. If the obliteration is not complete, namely something partially blocks the gut cavity, the symptoms are less visible, for example vomiting, slow weight loss, bad appetite, smaller amount of stool may be noticed.
Diagnosis:
If ileus is suspected, fast and exact diagnosis is very important for which profound physical examination followed by contrasty X-ray and abdominal ultrasound test are essential.
Treatment:
Usually, surgery is necessary as soon as possible (cutting or sometimes excising), and later conservative post-treatment.
